2024-02-06
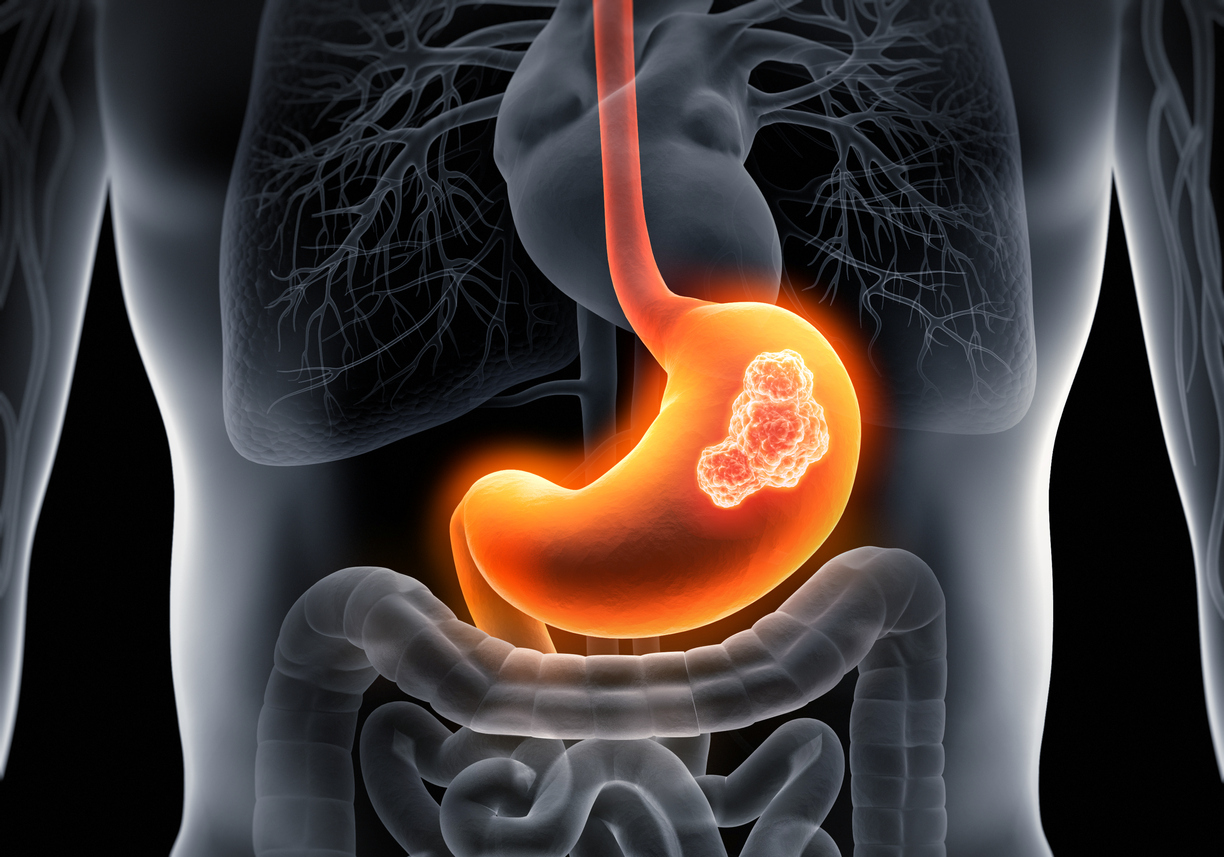
The role of Streptococcus anginosus in the progression of gastric tumors
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
The gastric mucosa of patients with gastric cancer is enriched in Streptococcus anginosus. In this study, the role of this bacterium in the pathogenesis of gastritis and gastric cancer was evaluated in mice. The bacterium colonizes the mouse stomach and induces acute gastritis. Progressively, gastritis becomes chronic, with parietal cell atrophy, mucinous metaplasia and dysplasia. In addition, Streptococcus anginosus infection accelerates the development of gastric tumors in mice. The bacterium disrupts gastric barrier function, promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis. The researchers clarified the cellular mechanisms involved and identified the TMPC-ANXA2-MAPK axis.
Last press reviews
Endometrial cancer: Is PARP bringing new hope?
By Ana Espino | Published on February 3, 2026 | 3 min read<br>
Hypertension: a new threshold, a new challenge

By Ana Espino | Published on January 30, 2026 | 3 min read<br><br>...
