2024-04-02
Tofacitinib in vitiligo
Dermatology and Venereology
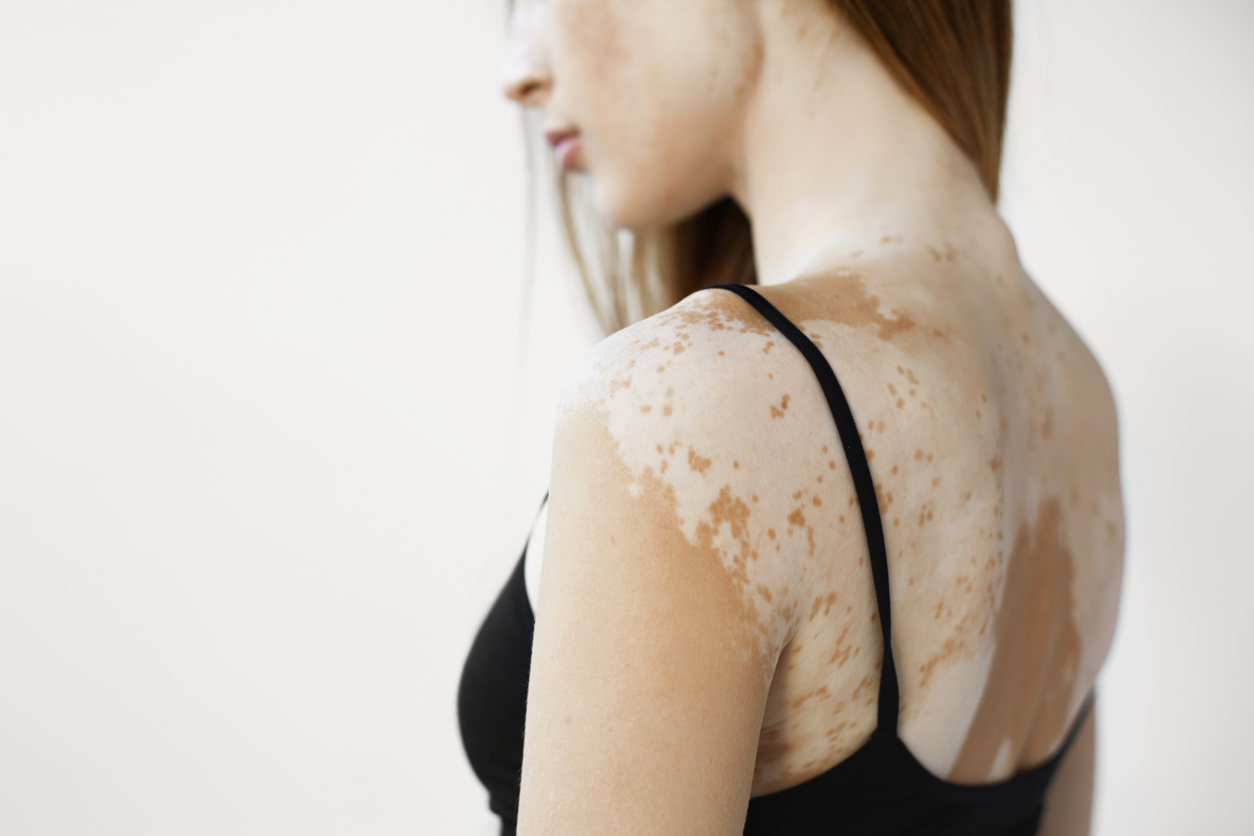
Vitiligo is a skin depigmentation disease resulting from the destruction of melanocytes, often concomitant with autoimmune diseases such as hyperthyroidism or systemic lupus erythematosus. The efficacy of available treatments for vitiligo varies considerably. In this case study, researchers report on a patient with vitiligo and systemic lupus erythematosus. After 30 days' treatment with tofacitinib, complete repigmentation of the white macular rash was achieved, with no adverse drug reactions. These results provide convincing evidence of the efficacy and safety of oral JAK inhibitors, such as tofacitinib, in the treatment of vitiligo.

Last press reviews
Could statins soothe inflammation?

By Ana Espino | Published on February 6, 2026 | 3 min read<br>
IAVI G004 trial: overview of a next generation HIV vaccine
By Carolina Lima | Published on February 5, 2026 | 3 min read
Liver, sugar, and pills: who's in control?
By Ana Espino | Published on February 4, 2026 | 3 min read<br>