2025-10-23
Virtual cognitive behavioral therapy: a digital shift in mental health care
Psychiatry
By Carolina Lima | Published on October 23rd, 2025 | 3 min read
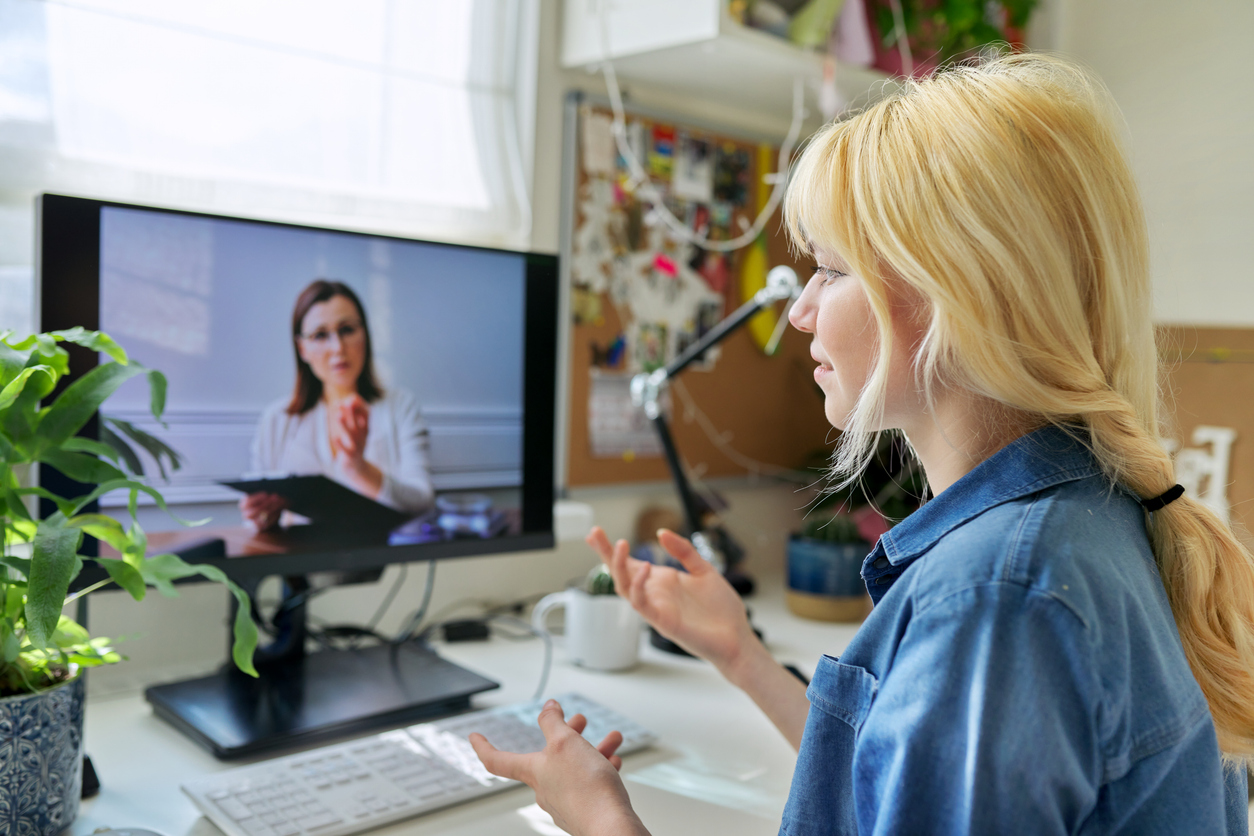
In recent years, mental health care has undergone a significant transformation, with digital tools reshaping how therapy is delivered. Among these innovations, virtual cognitive behavioral therapy (eCBT) has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional in-person therapy, offering flexibility, accessibility, and comparable clinical outcomes.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a well-established psychological treatment that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is widely used to treat conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and insomnia. eCBT refers to the delivery of CBT through digital platforms—such as video conferencing, mobile apps, or web-based programs—allowing patients to engage in therapy remotely. When adapted to virtual formats, eCBT retains the core principles of CBT while leveraging technology to reach more people.
The shift toward virtual therapy was accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many healthcare systems to adopt remote care models. However, the appeal of eCBT goes beyond necessity. It offers greater accessibility, especially for individuals in remote areas or those with mobility or scheduling constraints. It also reduces stigma, as patients can receive care privately from their homes.
A recent study published in BMC Psychiatry (Vizza et al., 2025) explored patient experiences with both in-person CBT and eCBT. The researchers identified five key themes: access, therapeutic relationship, satisfaction, environmental fit and empowerment.
The findings revealed that many patients appreciated the flexibility of eCBT, the ability to receive care from the comfort of their homes, and the sense of empowerment that came with managing their mental health digitally.
Despite its advantages, eCBT is not without limitations. The same study noted that some patients struggled with technological issues, such as poor internet connectivity or unfamiliarity with digital platforms, felt less connected to their therapists in virtual sessions or found it harder to stay engaged without the structure of in-person sessions. Building a strong therapeutic alliance in a virtual setting requires intentional effort and adaptation from clinicians.
Moreover, eCBT may not be suitable for individuals with severe mental health conditions or those in crisis. It also requires a certain level of digital literacy and self-motivation, which may not be present in all patients.
As digital health continues to advance, eCBT is likely to become a standard component of mental health care. Innovations such as AI-guided therapy, virtual reality exposure therapy, and personalized digital modules are already being tested and implemented. These tools aim to enhance engagement, improve outcomes, and make therapy more responsive to individual needs.
As we move toward more digital models of care, integrating virtual cognitive behavioral therapy (eCBT) into everyday mental health support must be done with care and intention. It’s not just about using new technology—it’s about making sure it truly works for the people who need it. That means continuing to invest in clinical research, training therapists to adapt their approach online, and protecting patient privacy and consent every step of the way.
eCBT isn’t meant to replace face-to-face therapy. Instead, it’s an opportunity to offer more choices—especially for patients who face barriers to traditional care. When thoughtfully implemented, eCBT can make mental health support more inclusive, flexible, and better suited to the diverse realities of patients’ lives.
About the Author – Carolina Lima
Carolina is a specialist in Anaesthesiology with a deep passion for learning and sharing medical knowledge. Dedicated to advancing the field, Dr. Lima strives to bring fresh, evidence-based insights to the medical community. Viewing medicine not merely as a profession but as a lifelong journey of continuous learning, Dr. Lima is committed to making complex information clear, practical, and useful for healthcare professionals around the world.
In recent years, mental health care has undergone a significant transformation, with digital tools reshaping how therapy is delivered. Among these innovations, virtual cognitive behavioral therapy (eCBT) has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional in-person therapy, offering flexibility, accessibility, and comparable clinical outcomes.
What Is eCBT?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a well-established psychological treatment that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is widely used to treat conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and insomnia. eCBT refers to the delivery of CBT through digital platforms—such as video conferencing, mobile apps, or web-based programs—allowing patients to engage in therapy remotely. When adapted to virtual formats, eCBT retains the core principles of CBT while leveraging technology to reach more people.
Why is eCBT gaining popularity?
The shift toward virtual therapy was accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many healthcare systems to adopt remote care models. However, the appeal of eCBT goes beyond necessity. It offers greater accessibility, especially for individuals in remote areas or those with mobility or scheduling constraints. It also reduces stigma, as patients can receive care privately from their homes.
A recent study published in BMC Psychiatry (Vizza et al., 2025) explored patient experiences with both in-person CBT and eCBT. The researchers identified five key themes: access, therapeutic relationship, satisfaction, environmental fit and empowerment.
The findings revealed that many patients appreciated the flexibility of eCBT, the ability to receive care from the comfort of their homes, and the sense of empowerment that came with managing their mental health digitally.
Benefits of eCBT
- Accessibility: Removes geographic and logistical barriers, making therapy available to more people.
- Comfort: Patients often feel more relaxed in familiar environments, which can lead openness and engagement.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduces travel and overhead costs, making therapy more affordable.
- Scalability: Can be delivered to large populations through automated or semi-guided programs.
- Empowerment: Digital tools often include self-monitoring features that encourage active participation in treatment.
Challenges and limitations
Despite its advantages, eCBT is not without limitations. The same study noted that some patients struggled with technological issues, such as poor internet connectivity or unfamiliarity with digital platforms, felt less connected to their therapists in virtual sessions or found it harder to stay engaged without the structure of in-person sessions. Building a strong therapeutic alliance in a virtual setting requires intentional effort and adaptation from clinicians.
Moreover, eCBT may not be suitable for individuals with severe mental health conditions or those in crisis. It also requires a certain level of digital literacy and self-motivation, which may not be present in all patients.
The future of eCBT
As digital health continues to advance, eCBT is likely to become a standard component of mental health care. Innovations such as AI-guided therapy, virtual reality exposure therapy, and personalized digital modules are already being tested and implemented. These tools aim to enhance engagement, improve outcomes, and make therapy more responsive to individual needs.
Conclusion
As we move toward more digital models of care, integrating virtual cognitive behavioral therapy (eCBT) into everyday mental health support must be done with care and intention. It’s not just about using new technology—it’s about making sure it truly works for the people who need it. That means continuing to invest in clinical research, training therapists to adapt their approach online, and protecting patient privacy and consent every step of the way.
eCBT isn’t meant to replace face-to-face therapy. Instead, it’s an opportunity to offer more choices—especially for patients who face barriers to traditional care. When thoughtfully implemented, eCBT can make mental health support more inclusive, flexible, and better suited to the diverse realities of patients’ lives.
Read next: One session, one trigger?
About the Author – Carolina Lima
Anaesthesiology specialist
Carolina is a specialist in Anaesthesiology with a deep passion for learning and sharing medical knowledge. Dedicated to advancing the field, Dr. Lima strives to bring fresh, evidence-based insights to the medical community. Viewing medicine not merely as a profession but as a lifelong journey of continuous learning, Dr. Lima is committed to making complex information clear, practical, and useful for healthcare professionals around the world.

Last press reviews
High-grade astrocytoma: combining two treatments opens a new therapeutic avenue
By Elodie Vaz | Published on March 9, 2026 | 3 min read<br><br>High-...

