2024-03-04
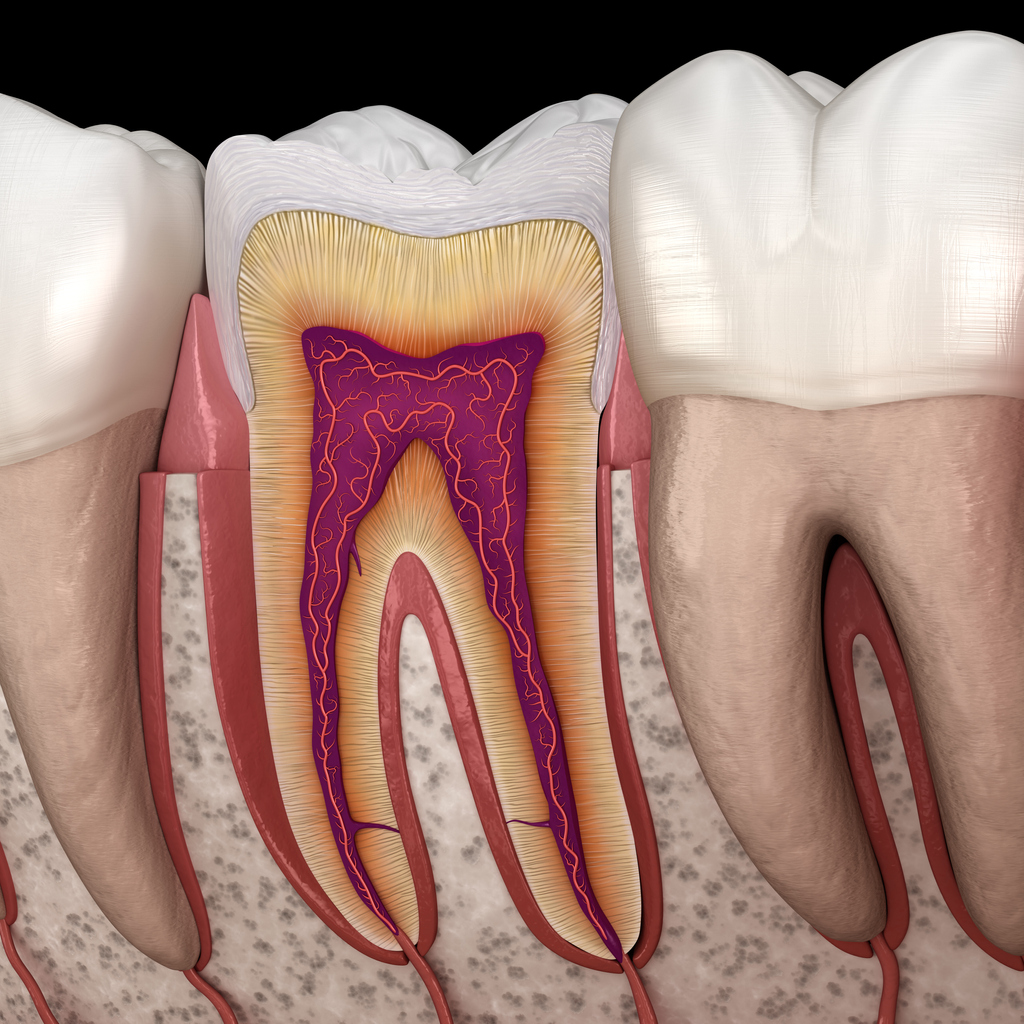
A new hydrogel for dental pulp regeneration
Dentistry
Source(s) :
Y Han et al. Injectable Tissue-Specific Hydrogel System for Pulp-Dentin Regeneration. J Dent Res. 2024 Feb 27:220345241226649. ;
Last press reviews
High-grade astrocytoma: combining two treatments opens a new therapeutic avenue
By Elodie Vaz | Published on March 9, 2026 | 3 min read<br><br>High-...

