2024-03-06
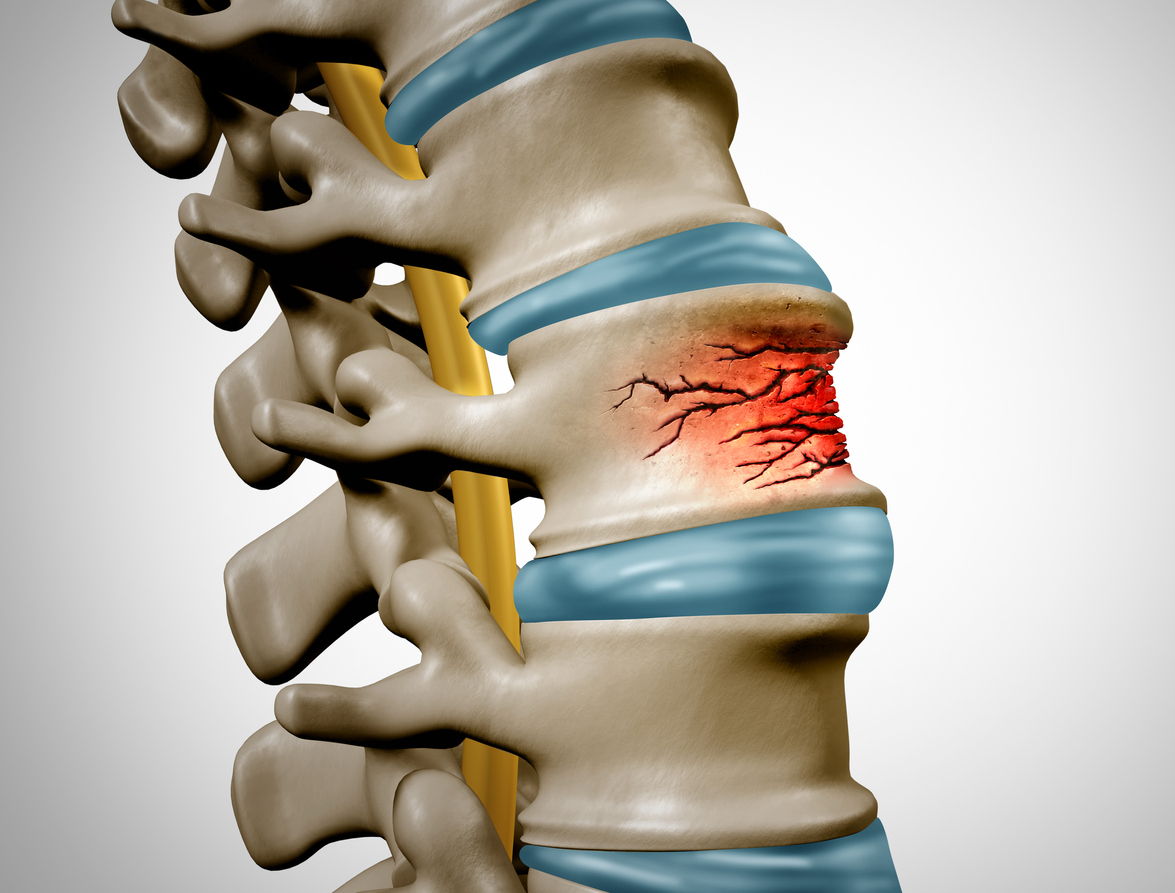
Inflammation in fractures of the lumbar vertebrae and pelvis
Surgery
Fractures of the lumbar vertebrae and pelvis are frequently associated with peripheral ligament damage. Previous studies have reported that the fracture site is generally associated with the secretion of inflammatory proteins. In this study, researchers used two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses to investigate causal links between fractures, ligament damage and 91 circulating inflammatory proteins. Several inflammatory proteins showed causal links with lumbar and pelvic vertebral fractures and the occurrence of peripheral ligament damage. These new data could help to better predict this risk.
Last press reviews
Arterial hypertension: radar blood pressure monitors for greater accuracy

By Elodie Vaz | Published on February 20, 2026 | 3 min read<br>
Safe Sex 2.0: which digital tools actually work?

By Ana Espino | Published on February 20, 2026 | 3 min read<br><br>
Stem cell transplantation: ai to predict severe complications

By Elodie Vaz | Published on February 18, 2026 | 3 min read<br>