2024-02-21
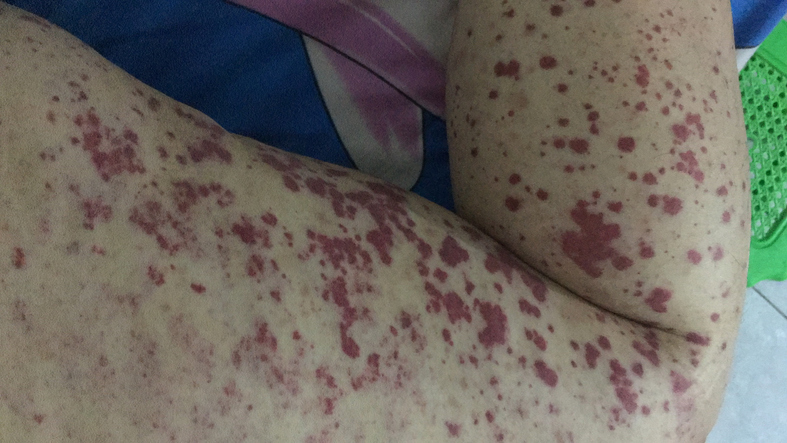
ANCA-associated vasculitides
Cardiology and Vascular Medicine
Source(s) :
Andreas Kronbichler et al. Diagnosis and management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Lancet. 2024 Feb 17;403(10427):683-698. ;
Last press reviews
Hypertension: a new threshold, a new challenge

By Ana Espino | Published on January 30, 2026 | 3 min read<br><br>...
Allergies: the molecular revolution is underway

By Ana Espino | Published on January 29, 2026 | 3 min read<br>
