2020-11-26
Early introduction of gluten to prevent celiac disease
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
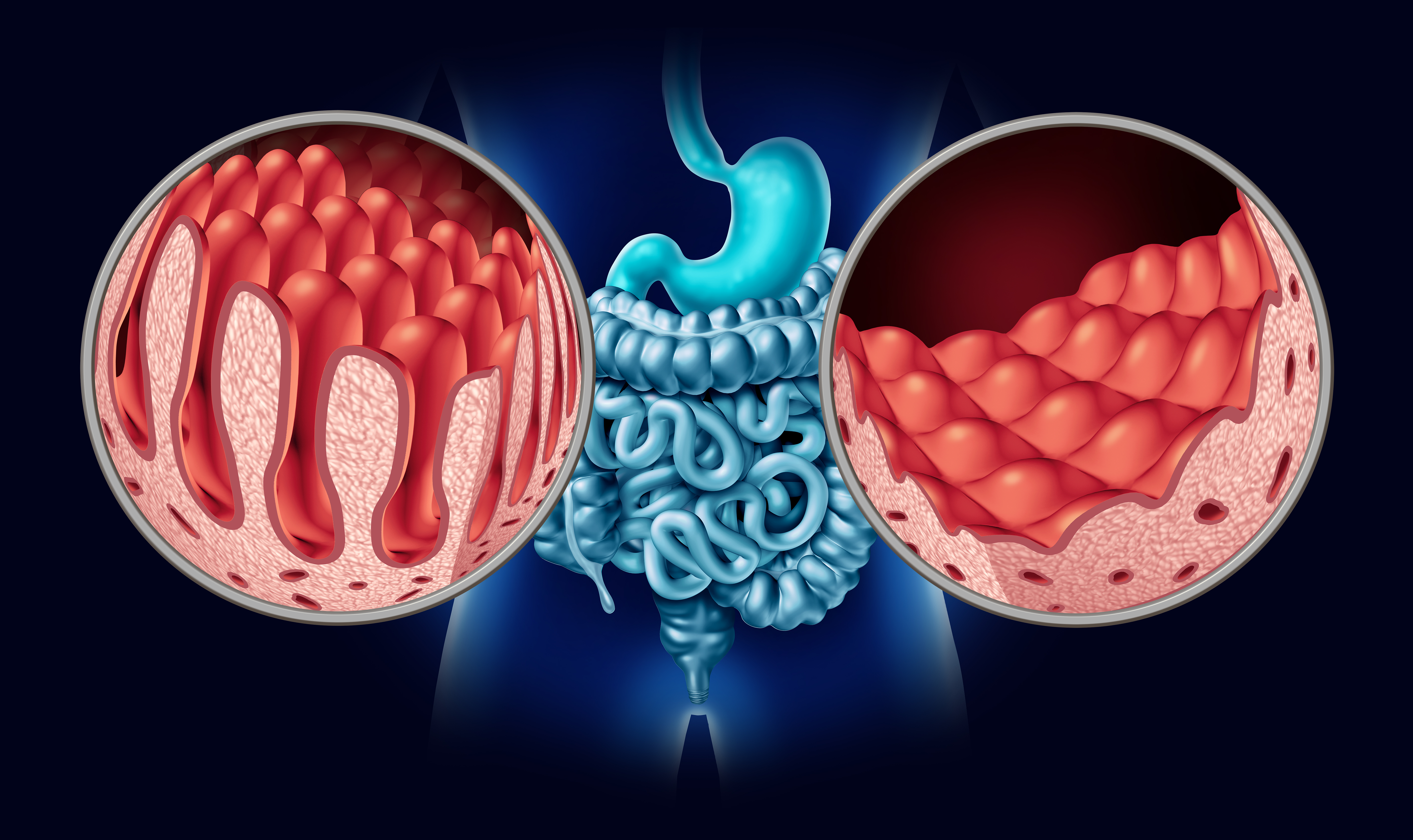
There is currently no preventive treatment for this disease, which affects nearly 1% of the population. In 2008, the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) recommended introducing wheat into the diet of infants between 4 and 6 months of age to help prevent celiac disease. However, there was little evidence to support the existence of a link between gluten introduction and the prevalence of celiac disease. Researchers have recently demonstrated this relationship through a randomized clinical trial involving 1,004 infants aged 4 months, whose diets were monitored until they reached 6 months of age. The diets of 488 children included six allergenic foods (peanut, sesame, hen's egg, cow's milk, cod, and wheat), while the diets of the remaining 516 infants were allergen-free. A diagnosis of celiac disease was confirmed in a significantly higher number of children who had not consumed allergens (1.4%) compared to those who had been exposed to allergens early on (0%; p = 0.002; Risk 1.4%; 95% Confidence Interval [0.6%–2.6%]). The results of this trial suggest that early gluten consumption may be considered a strategy for preventing celiac disease.
Source(s) :
JAMA Pediatrics, publié le 28/09/2020 ;
Last press reviews
Arterial hypertension: radar blood pressure monitors for greater accuracy

By Elodie Vaz | Published on February 20, 2026 | 3 min read<br>
Safe Sex 2.0: which digital tools actually work?

By Ana Espino | Published on February 20, 2026 | 3 min read<br><br>
Stem cell transplantation: ai to predict severe complications

By Elodie Vaz | Published on February 18, 2026 | 3 min read<br>